Cervical cancer is among the few cancers which frequently affect women all over the world. This occurs in the lower section of uterus where cervical cells are grown. Therefore there is the need for screening and vaccination with a view of having early intervention and treatment of the disease if it occurs. This article will therefore describe the symptoms and diagnosis of cervical cancer, and vaccines that are in the market.

Understanding Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer occurs due to certain changes taking place in the normal cells that are present in the cervix region of the woman’s reproductive tract. important two primary types of cervical cancer are:
Squamous cell carcinoma:
This is also known as epidermoid carcinoma. These cell starts over-growing on the outer lining of the skin, this is a type of skin cancer. It is the second most malignancy which is increasing world wide
Adenocarcinoma:
This is a type of cancerous tumor which occurs in the several parts of the body. This cancers starts in the glands that line inside the body organs organs like breast, prostate, lings and colon.
Cervical Cancer Symptoms
Often, cervical cancer has no early symptoms and therefore early screening is encouraged to identify this cancer in its early stages. However there are signs and symptoms of the disease as it progresses, they include:
1. Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding
Some of the signs includes any abnormal vaginal bleeding; for instance, having bleeding in between the monthly period or after having sexual relations. In addition, postmenopausal women who develop vaginal bleeding should consult a doctor or health care provider.
2. Unusual Vaginal Discharge
Symptoms of cervical cancer include a change in the normal type and amount of white discharge and if the woman has cervical cancer she may experience a watery bloody discharge which has a foul smell. This symptom may even worsen with the progression of the cancer especially to the advanced stages.
3. Pelvic Pain
Menstrual cycle irregularity was reported mainly in primary cervical cancer while lower abdomen and/or pelvis pain in the absence of menstrual cycle was attributed to the advanced cervical cancer. Some of the women may also have a problem of dyspareunia, which is the feeling of pain during intercourse.
4. Dysuria or Pain While Urinating
If cervical cancer has reached the next stage, that is the local invasion of nearby tissues or organs, then the cancer may cause painful or uncomfortable urination or frequent need to urinate. This happens where the pressure being exerted by the tumor affects other surrounding organs.
5. Lower Back Pain
If the lower back pain is chronic and is felt in the legs then it may be suggestive of extension of cervical cancer towards the tissues or nerves surrounding the area.
These symptoms can be also observed in other less severe conditions, therefore it is important to mention it. In other words, if a person has one or more of these symptoms, this does not necessarily imply that the person has cervical cancer. However, if any of the mentioned symptoms persists then one should not hesitate to visit their physician.
Diagnosis of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is one of the diseases in which screening and diagnostic tests can identify the disease at an early stage. In cervical cancer, it is considered to advise women to adhere to some of the recommended measures that would help in early detection of the disease.
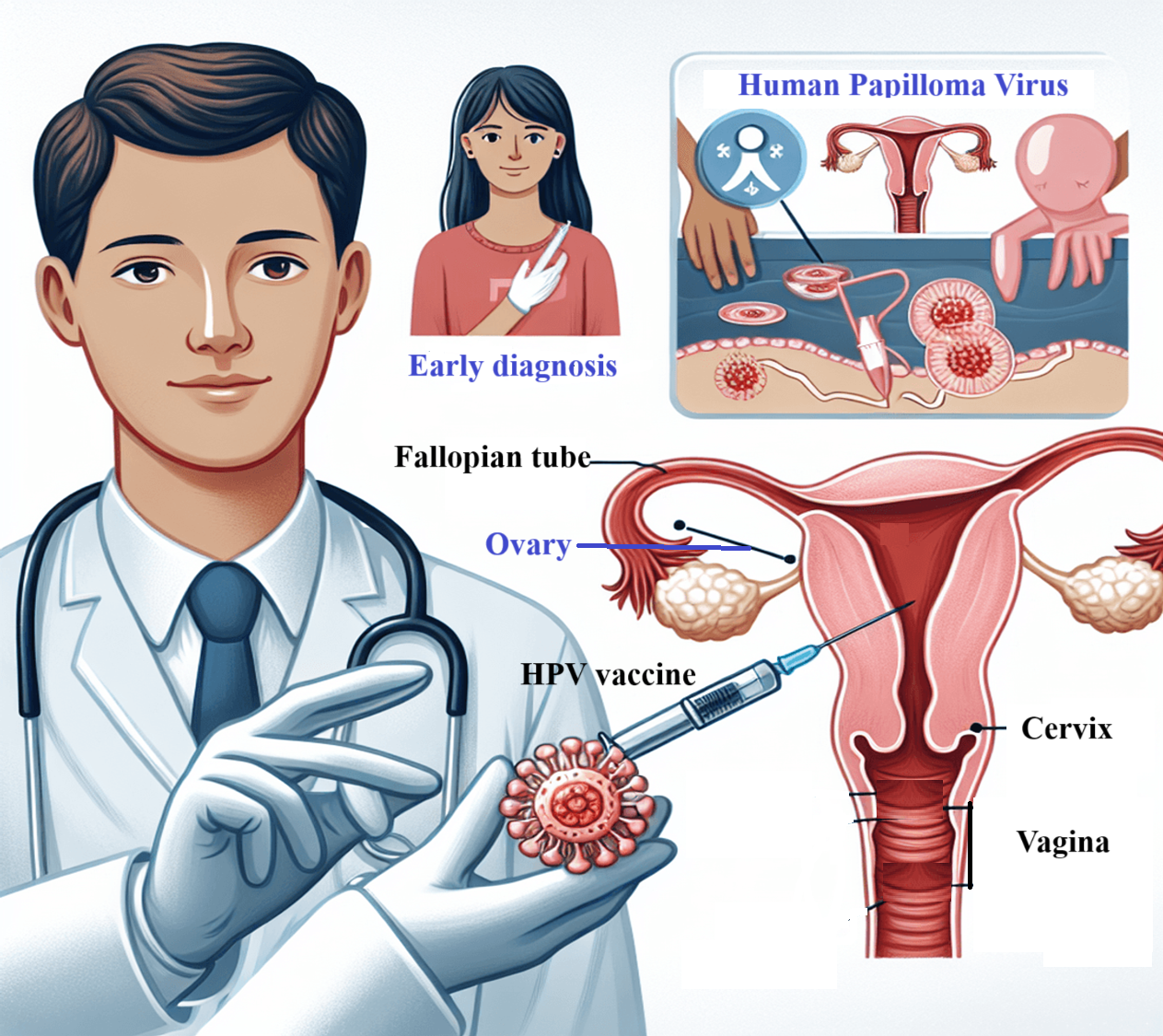
1. Pap Smear Test
Pap smear commonly known as a Pap test is the most effective way of diagnosing precancerous changes or cervical abnormalities. In this process, a health care worker scrapes cells from the cervix which is then analyzed under microscope in case there are changes that may cause cancer. Pap testing should start at the age of 21, and women should stay with testing that their doctor prescribes furthermore.
2. HPV(Human Papilloma Virus) Test
The HPV test is used to identify the existence of those HPV subtypes that are possibly to cause cervical cancer. This test can be done together with the conventional Pap smear or as a separate test, especially for women who are 30 years and above. An HPV test is positive does not mean a person will have cervical cancer however they are at a higher risk of developing it.
3. Colposcopy
In this procedure, a device called colposcope is employed to check the cervix for any cancer or precancerous cell growth. Sometimes, a definite diagnosis is made and tissue samples are also removed through biopsy for further examination.
4. Biopsy
A biopsy entails taking a small sample of cervical tissue with a view of establishing whether or not the tissue contains cancerous cells. There are several types of biopsies used to diagnose cervical cancer. There are several types of biopsies used to diagnose cervical cancer:
- Punch biopsy: This procedure involves taking out a tiny piece of tissue from the cervical region.
- Endocervical curettage: Collects cells from the Cervical canal.
- Cone biopsy: Adopts a lip-shaped excision of the tissue that forms a cone and whose size is larger than that of the punch biopsy.
- Imaging Tests
If cervical cancer is present then MRI, CT or PET scans can be carried out for staging of the cancer. It is useful to know this, so that doctors can come up with the right approach to the treatment.
Treatment for Cervical Cancer
When it comes to the treatment of cervical cancer the following are some of the options that are available.
- Surgery: Surgically excising the affected tissue for instance through of hysterectomy is also effective in treating the disease.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy that employs ionizing energy to destroy the cells.
- Chemotherapy: Treating cancer through usages of drugs that can either kill the abnormal cells or prevent their multiplication.
- Targeted therapy: Targets some vulnerable aspects of cancerous cells.
Preventing Cervical Cancer: HPV vaccines
The use of vaccines to prevent HPV has been noted has a strong weapon in the fight against cervical cancer. The vaccines that are available today are designed for the subtypes of HPV which are involved in a large number of cervical cancer cases.
1. Gardasil 9
The most common HPV vaccine in the world is Gardasil 9, this vaccine targets 9 types of the virus. This vaccine stipulates immunization against different types of HPV like 6, 11, 16, 18 etc. Adolescent’s should take Gardasil 9; the minimal age is 9 years old. It is usually applied in two or three doses in the span of three to six months if commenced at different ages.
2. Cervarix
Cervarix is another manufactured HPV vaccine that afford protection against two HPV types that are strongly associated with cervical cancer namely HPV 16 and HP 18. This medication is recommended for females only and is taken in three cycles, once in six months.
Who Should Get Vaccinated?
Further, the vaccine for the HPV is recommended for college students one dose at the age group 9 to14 and second dose to be schedule at 15 -20 years. The main objective is to eradicate the spread of virus as well as decrease in cervical cancer. The best time to give the vaccine is before the person gets involved in sexual life, since it is most effective (90%) in an individual who has not come into contact with the virus.
Cost of the HPV Vaccine
The price of the HPV vaccine differs from one country to the other, the doctor who prescribes it and whether the patient needs to bear the costs or the costs will be covered by insurance or other government programs. In the United States, each dose of Gardasil 9 costs around $250 with the series consisting of two or three doses making the overall cost be around $500 to $750.
Some of them include Medicaid and many other insurance plans that can ensure that the costs of the vaccine are covered. In the same way, the Government through programs like the Vaccines for Children Program (VFC) that offers free vaccines to children below 19.
Conclusion
Cervical cancer is one disease that is preventable by being aware of such signs/ symptoms, practicing regular screening, and taking the HPV vaccine.. Early signs should be realized and one should go for routine Pap smears or HPV tests so as to avoid the building up of advanced cervical cancer. The availability of a vaccine for HPV has been a major boost in the fight against cervical cancer across the world. Although the vaccine costs may be an issue in some areas, the intensification of campaigning for the increased uptake of the vaccine is on the rise.